Importance of balanced diets
Society faces a dual burden of malnutrition and over-nutrition-related disorders with hidden hunger. An adequate and well-balanced diet regarding calories, macro, and micronutrients is critical for a healthy life. Increased stress, pollution, adaptive changes in the genetic makeup of Indians due to feast and famine conditions in the past and faulty lifestyles are responsible for the rise in obesity-related disorders. Calorie restriction (CR) without micronutrient deficiency is a dietary regimen reported to have beneficial effects by decreasing oxidative stress and improving insulin sensitivity. Different food restrictions or fasts are practised worldwide for religious and health benefits like reduction in body weight and biochemical markers of metabolic syndrome. Fasting decreases post-prandial oxidative stress. Highly restrictive diet plans should be avoided as they may lead to micronutrient deficiencies.
Nutrition problems in modern society
Malnutrition refers to not receiving proper nutrition, and it does not distinguish between the consequences of too many nutrients or the lack of nutrients, both of which impair overall health. Over-nutrition is a chronic condition where food intake exceeds dietary energy requirements, resulting in obesity.
Obesity and covid-19
In a Survey conducted by NHFS in 2020, it was found that obesity is increasing in India. People who are obese are more prone to respiratory diseases and COVID-19. During this Pandemic, it was found that there was a higher admission rate of obese people in hospitals, and the Mortality rate due to COVID-19 was also increased. Hence, it is the need of the hour to work on Obesity and reduce it.
The measure of healthy weight
Nutrition plays a vital role in reducing Obesity. A person’s weight can be measured by adequate dietary intake. People with a BMI of more than 25 are considered obese. The Basal Metabolic Rate (BMR), a precisely defined measure of the energy expenditure necessary to support life, is determined under controlled and standardised conditions shortly after awakening in the morning, at least 12 hours after the last meal, and with a comfortable room temperature. Because of practical considerations, the BMR is rarely measured; the resting energy expenditure (REE) is determined under less stringent conditions, with the individual resting comfortably for about 2 to 4 hours after a meal. In practice, the BMR and REE differ by no more than 10 per cent. The REE is usually slightly higher, and the terms are used interchangeably.
Waist circumference measurement
The physiological body composition of both male and females are different. Females have more body fat than males. Hence, sometimes, the Criteria of BMI need to be more. Therefore, the following criterion we can use is the waist circumference measurement, as abdominal fat increases health risk more than fat on other parts of the body. 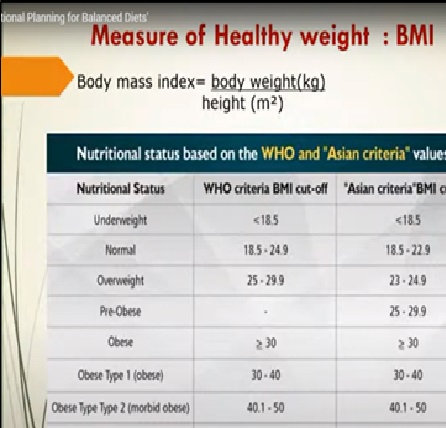
Metabolic Healthy Obese
People with obesity develop additional health problems known collectively as metabolic syndrome. However, not everyone with obesity has these complications. Some people call this Metabolically Healthy Obesity. 20% of people in India are under healthy obese, which means they do not have any other problems apart from obesity. For this reason, anyone with obesity should speak to their Dietician for advice. The doctor will likely suggest an action plan to reduce the person’s BMI.
Nutritional Requirements
The nutritional requirements of the body depend on several factors: –
- Energy expenditure
- Body composition and nutrient reserve.
- Growth need
- Climatic condition
- Food availability
- Dietary habits and preferences.
Balanced diets for adults
The recommended dietary allowance of nutrients for the country’s population is based on the current knowledge of nutritional requirements of different ages, sex groups, and countries’ food and dietary habits. RDA is used to formulate nutritional guidelines for individuals and groups and plan national food and agricultural strategies.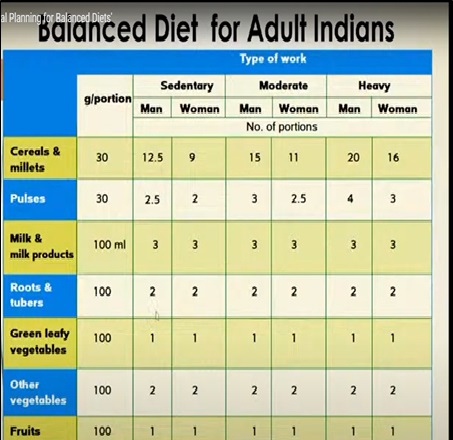
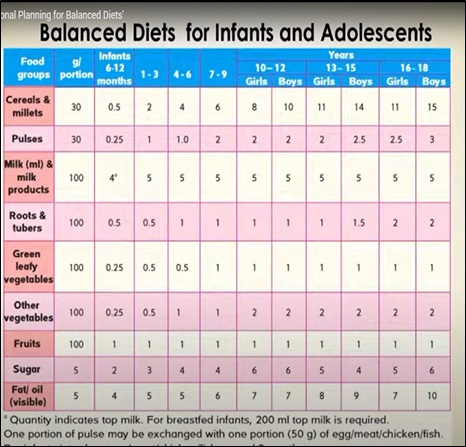
Balanced diets for infants and adolescents
My Plate Concept by ICMR
The plate, designed by the ICMR-National Institute of Nutrition, recommends sourcing macronutrients and micronutrients from a minimum of 8 food groups per day to achieve a balanced diet that would fulfil the required calorie or energy needs of Indians.
Nutritional Oxidative Stress
Nutritional oxidative stress describes an imbalance between the pro-oxidant load and the antioxidant, defined as a consequence of excess oxidative gear or inadequate supply of the organism with nutrients; the term dietary oxidative stress is often used synonymously.
Postprandial oxidative stress
Postprandial oxidative stress is characterised by an increased susceptibility of the organism toward oxidative damage after consuming a meal rich in lipids and carbohydrates. Thus, macronutrients affect the redox balance in the organism.
Conclusion
Nutrition is a critical part of health and development. Better nutrition is related to more robust immune systems and a lower risk of non-communicable diseases. Malnutrition, in every form, presents significant threats to human health. Hence, one should maintain adequate nutrition for health.






